
Stanford: Fintech Maintains Position as Third Biggest AI Investment Focus Area
by Fintechnews Switzerland April 25, 2023In 2022, global private investment in artificial intelligence (AI) companies reached US$91.9 billion, a 18-fold increase compared with 2013. Of that sum, fintech companies secured the third largest amount, raising a total of US$5.5 billion, a new report released by the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) says.
The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, released on April 03, sheds light on the impact and progress of AI over the past year, looking at trends in research and development (R&D), technical performance, ethics, economics, policy, public opinion, and education.
According to this year’s report, fintech maintained its position as the third largest focus area for AI investment, securing 6% of global AI funding in 2022. Fintech followed medical and healthcare, the year’s top AI focus area with US$6.1 billion raised, and data management, processing and cloud with total private investment reaching US$5.9 billion.
Nearly all AI focus areas recorded a decline in private investment last year, reflective of the global venture capital (VC) downturn. Investment in both AI fintech and AI for the medical and healthcare sector declined by 46% in 2022 each. Investment in AI data management, processing and cloud, meanwhile, fell 51.6%.
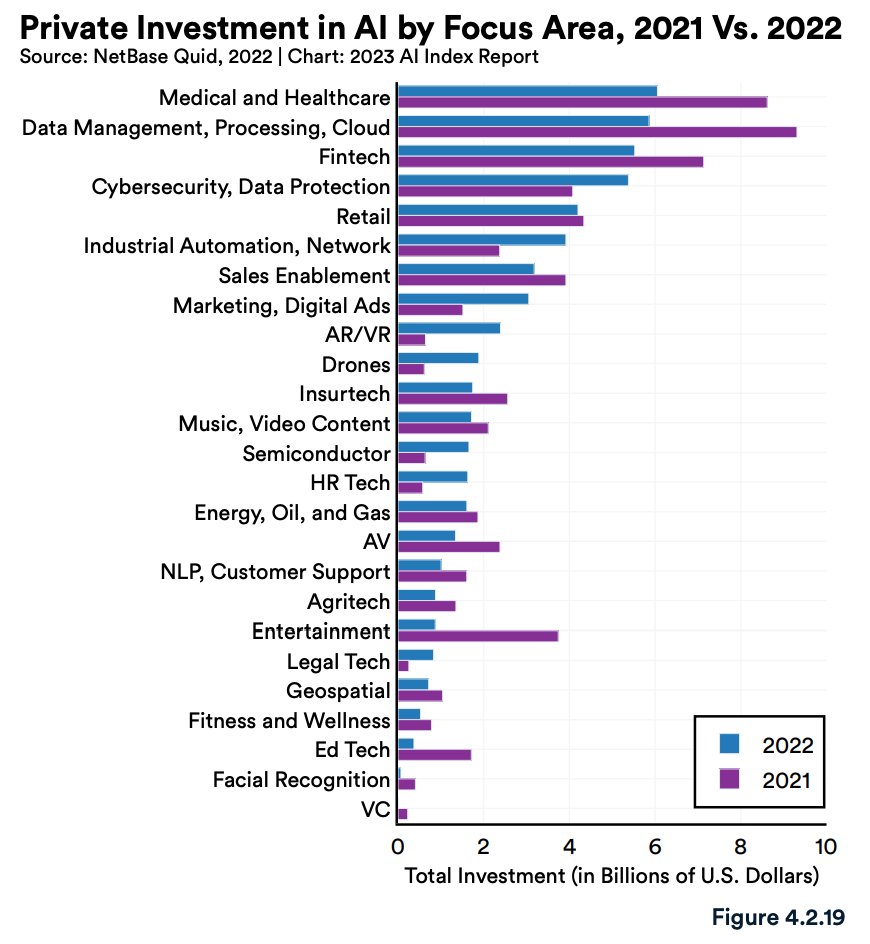
Private investment in AI by focus area, 2021 versus 2022, Source: The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence
Globally, AI private investment declined by 26.7% in 2022 while the broader corporate investment landscape, which also includes AI mergers and acquisitions (M&A), minority stakes and public offerings, pulled back by 31.3%.
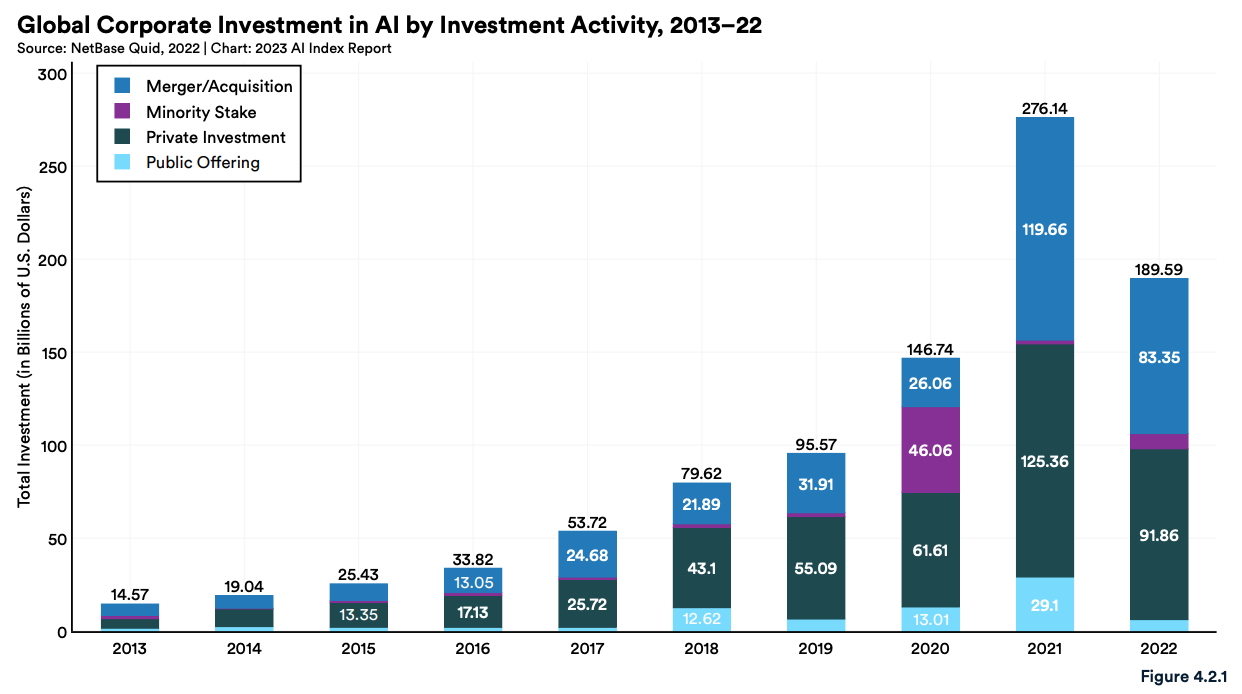
Global corporate investment in AI by investment activity, 2013-2022, Source: The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence
Despite the downturn, AI fintech recorded some notable deals in 2022. These included the US$8 billion purchase of Avast by NortonLifeLock in the year’s third largest AI M&A transaction; the US$1.48 billion minority stake event for Grupo de Inversiones Suramericana, the second biggest AI deal of this kind in 2022; and the US$820 million private investment secured by Faire Wholesale, the second largest AI private investment deal in the US last year.
AI moves to era deployment
The past year has seen AI reach a new level of maturity and shift towards deployment. New large-scale AI models are being released on a regular basis and are posting state-of-the-art results, the report says.
These models, which include chatbot ChatGPT, text-to-image models like DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion, and text-to-video systems like Make-A-Video, are capable of accomplishing an increasingly broad range of tasks and are demonstrating remarkable capabilities in question answering, and the generation of text, image, and code.
Generative AI, in particular, have been a hot topic in the tech sector over the past year, a trend that was fueled by the release of ChatGPT.
ChatGPT is a highly advanced AI language model developed by OpenAI that can generate human-life text responses to questions and prompts. The tool, which went viral last year, is capable of articulating answers across many domains of knowledge and can handle complex queries, debug computer programs, compose music, write poetry, and much more.
ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly active users months after its launch, making it the fastest-growing consumer application in history.
AI adoption on the rise
According to the Standard HAI report, AI usage has rapidly grown in the past half-decade. In 2022, half of the organizations surveyed by McKinsey reported having adopted AI in at least one business unit or function, up significantly from 20% in 2017.
In the financial services industry, product and/or service development was found to be the function AI capabilities were the most commonly implemented (31%), followed by service operations (24%) and strategy and corporate finance (23%).
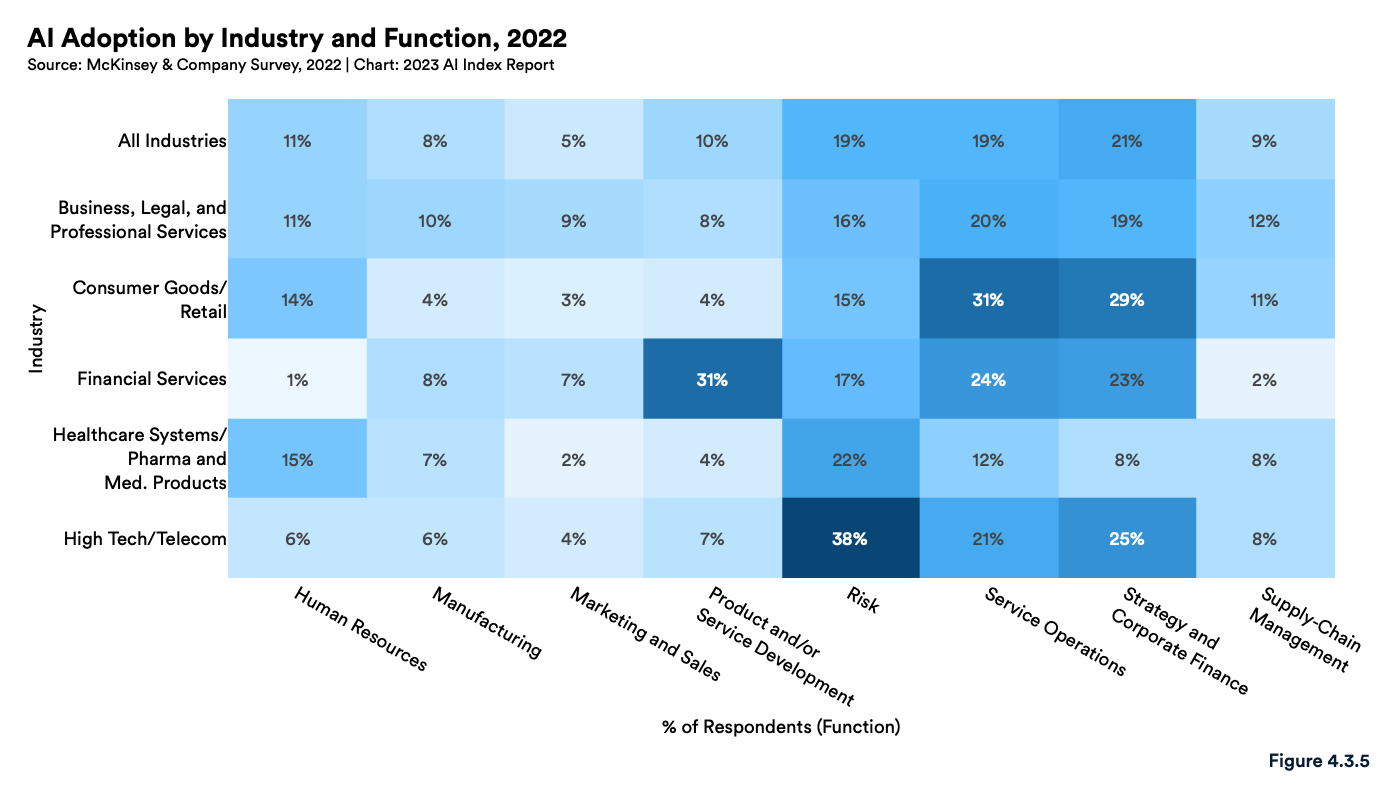
AI adoption by industry and function, 2022, Source: The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence
Looking at AI capabilities, robotic process automation had the highest rate of embedding within financial services (47%). Natural-language (NL) text understanding came in second at 42%, followed by virtual agents with an adoption rate of 33%.
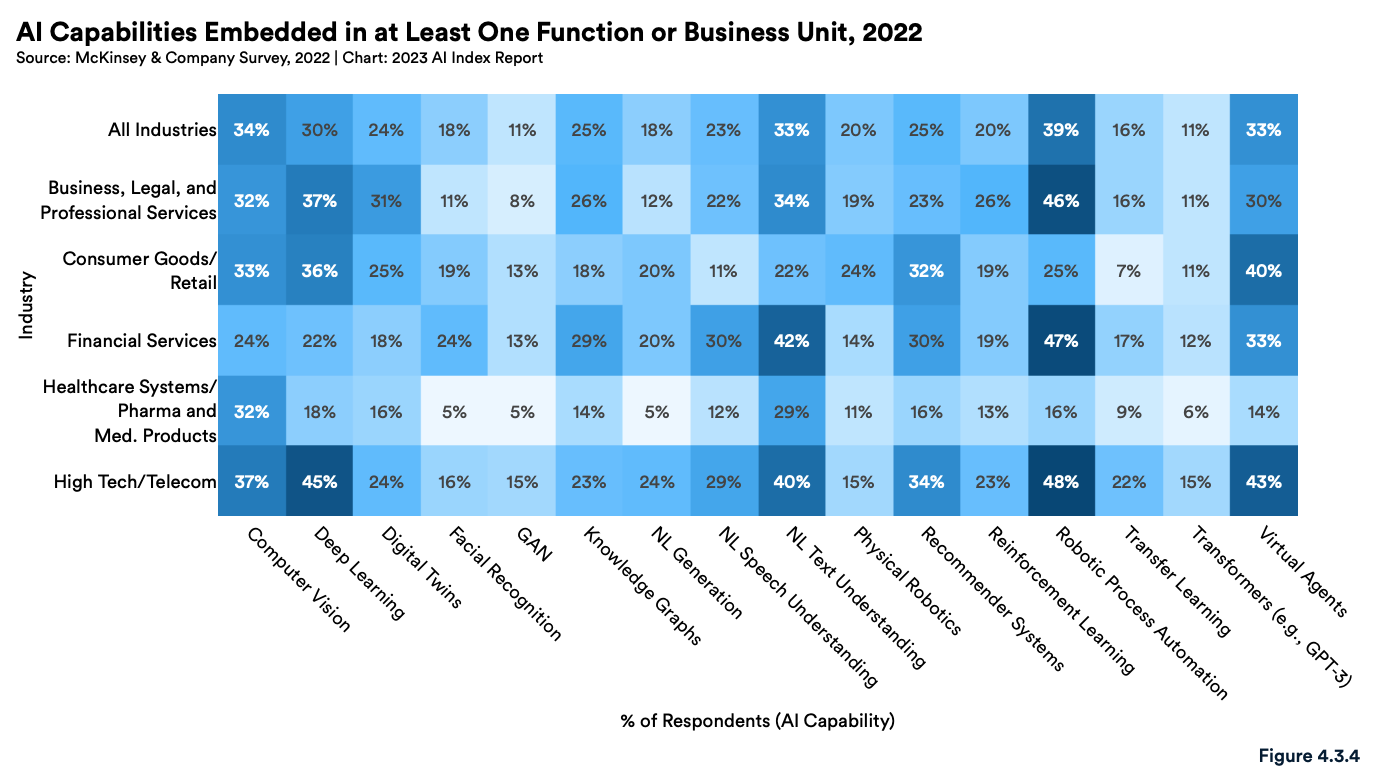
AI capabilities embedded in at least one function or business unit, 2022, Source: The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence
Organizations reported AI adoption has led to both cost decreases and revenue increases. On the cost side, the adoption of AI has most impacted supply chain management (52%), service operations (45%), risk (43%) and strategy and corporate finance (43%), the study found.
On the revenue side, the functions that most respondents saw increases in revenue as a result of AI adoption were marketing and sales (70%), product and/or service development (70%), and strategy and corporate finance (65%).
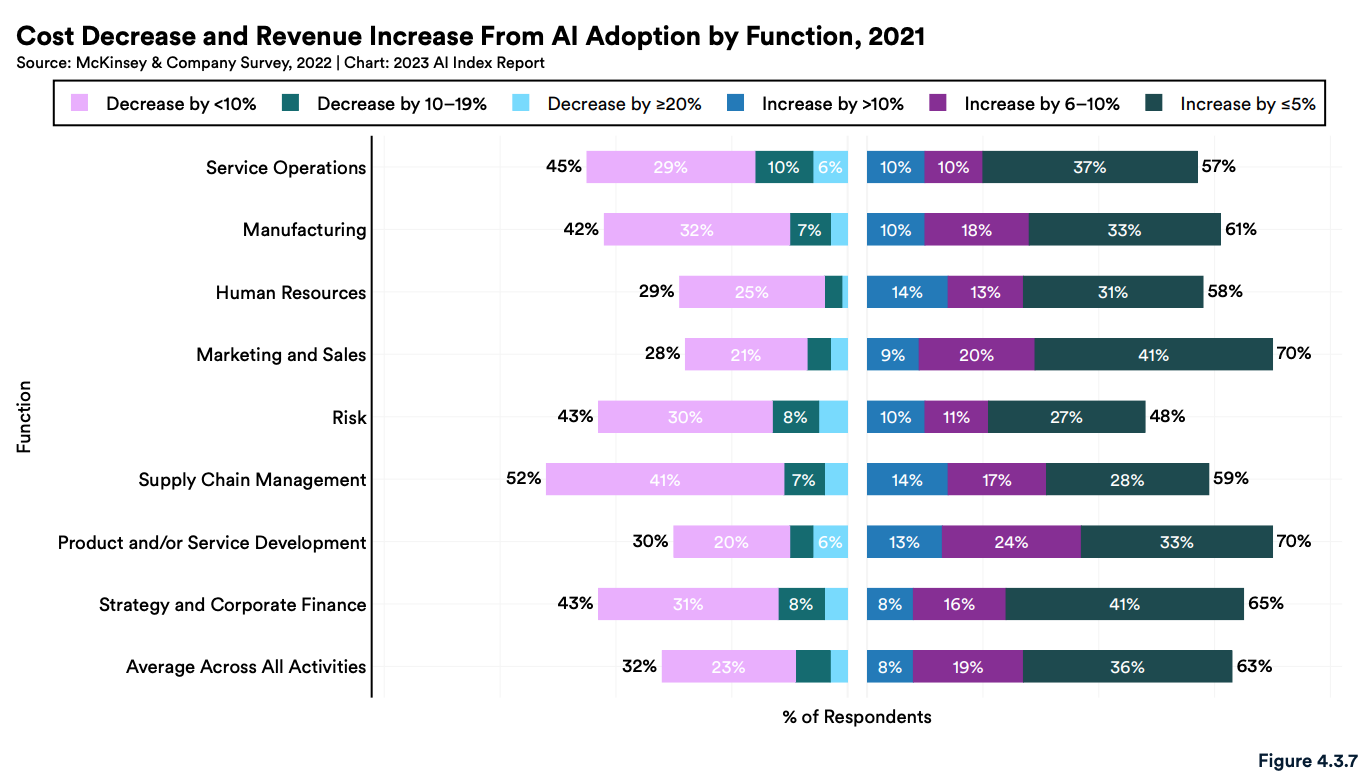
Cost decrease and revenue increase from AI adoption by function, 2021, Source: The Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2023, Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence





