
COVID-19 Crisis to Substantially Transform the Payments Landscape: McKinsey
by Fintechnews Switzerland April 30, 2020COVID-19 will have a long-lasting impact on all industries, and the payments sector will be no exception, according to a report by McKinsey & Company.
The use of cash and other paper payment methods is already rapidly declining with withdrawals at ATMs being down by more than 50% in many European countries. Meanwhile, contactless payments are rising strongly. These new consumer habits will become more and more ingrained and companies in the space should prepare themselves for some fundamental changes, the consultancy firm said in a paper released in March.
Digital wallet solutions will expand beyond just payments to include features such as digital IDs and transaction monitoring and reporting, and physical means of payments will continue to decline, putting pressure on companies to develop innovative solutions that ensure universal access for unbanked populations, it said.
Meanwhile, online commerce will continue to grow as an increasing number of offline businesses seek a digital future. This will require industry participants to rapidly build out omnichannel capabilities that bridge payments in any environment, physical or digital.
But it is not just payments, McKinsey said, as the COVID-19 pandemic is expected to shake up the fintech industry as a whole, eliminating initiatives that lack clear long-term economic viability, and pushing for greater market consolidation.
According to CB Insights, fintech funding has been down since December 2019, showcasing the impact that the COVID-19 outbreak has had on startup funding. Fintech companies in the space are projected to raise about US$6 billion in Q1’20, a level not seen since 2017.
COVID-19 takes a toll on payments revenues
Revenue growth in global payments is expected to turn negative instead of growing 6% as initially projected. Activity could drop by as much as 8 to 10% of total revenues, or a reduction of US$165 billion to US$210 billion, McKinsey projects.
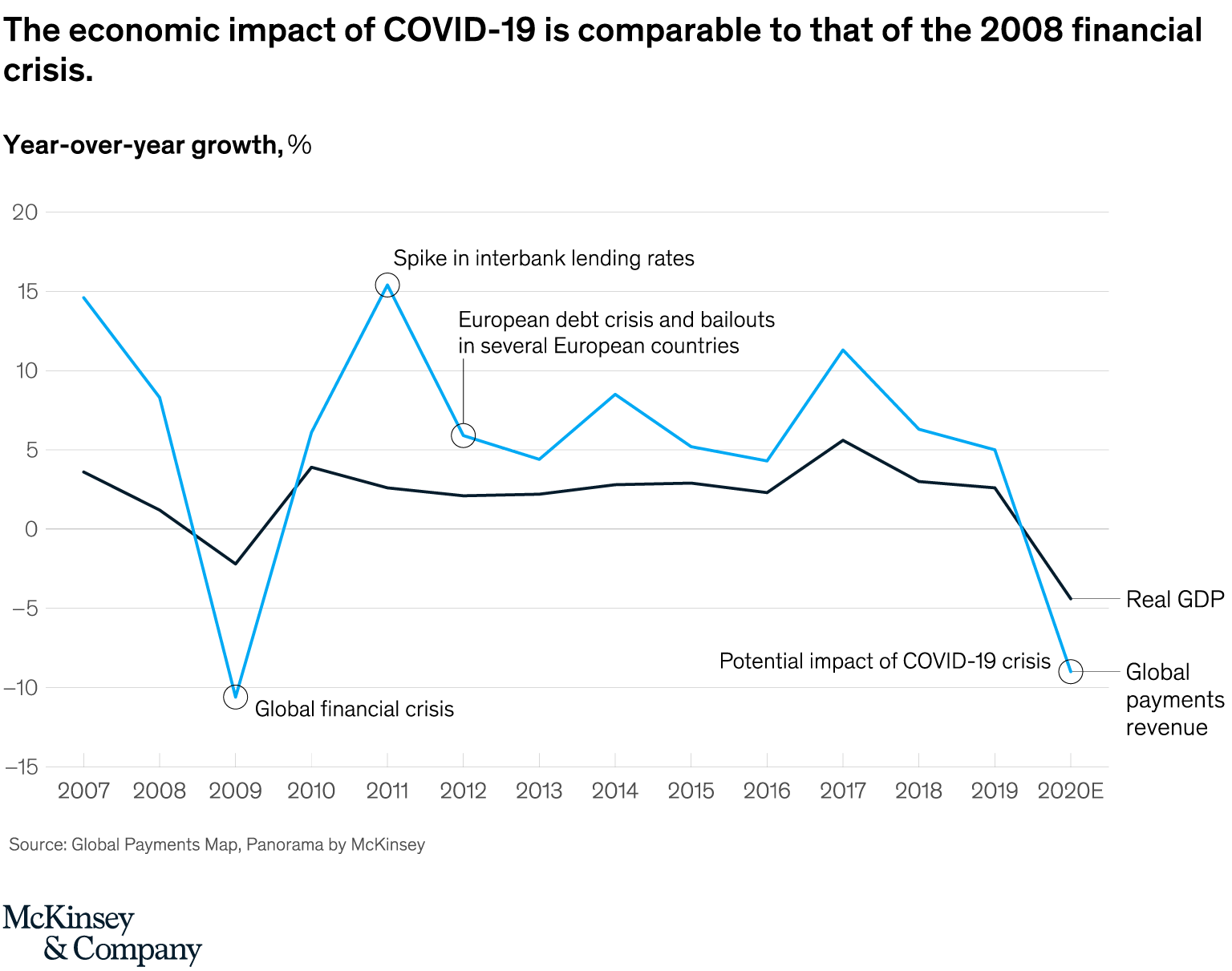
The economic impact of COVID-19 is comparable to that of the 2008 financial crisis. Source: Global Payments Map, Panorama by McKinsey
In a relatively optimistic scenario where the virus would be contained after an economic lockdown of two to three months in Europe and the US, payments revenues would decline, at most, US$165 billion as global GDP would drop 1.5%, the firm projects.
In a more pessimistic scenario characterized by a muted recovery, resurgence of the virus in China, and continued spread in the US and Europe, global payments revenues would decline in excess of US$210 billion while global GDP would contract by 4.7%.
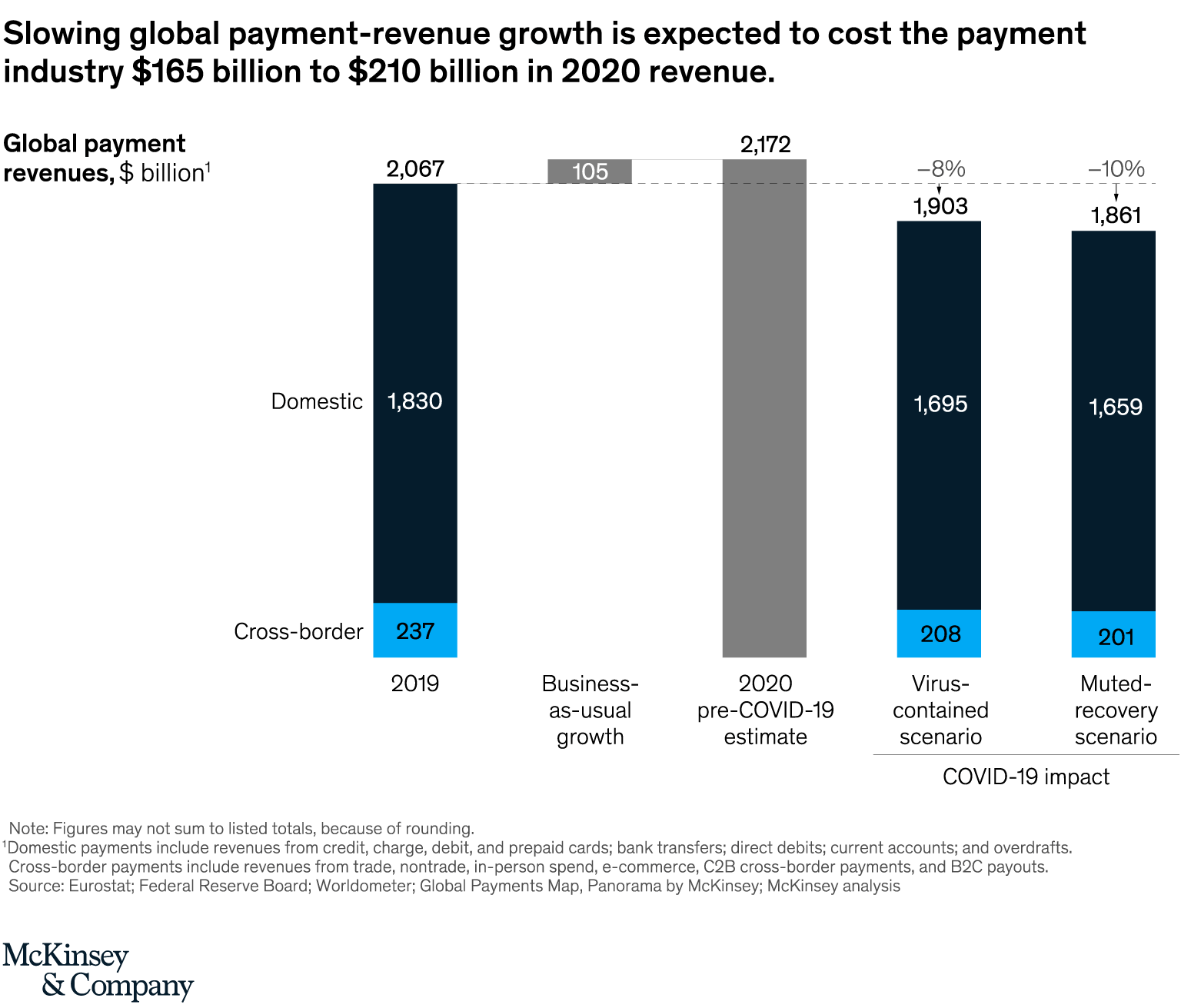
Slowing global payment-revenue growth is expected to cost the payment industry US$165 billion to US$210 billion in 2020 revenue. Source: McKinsey
Breaking down the different components behind the projected decline in global payments revenues, McKinsey predicts a drop by 25 to 30% in cross border consumer-to-business (C2B) transactions driven by the disruption of travel and tourism. Meanwhile, classic point-of-sale (POS) payments volumes could decline by as much as 30 to 40% in the short term.
The firm also forecasts a drop in cross border business-to-business (B2B) transactions with border closure substantially impacting global commerce.





