Let’s get serious about this hyped technology: the momentum is now
The buzz surrounding Blockchain is comparable to that surrounding the internet in the early 1990s
Do you remember the nineties? Everyone was talking about the internet and its potential, about life changing moments, about disruption, but no one could imagine what is possible? And today: our lives changed fundamentally. Everyone is communicating everywhere, new business models emerged – just to name the platform model, perfectly turned into revenue streams by AGFA – Apple, Google, Facebook and Amazon. The company AGFA overslept this life changing moment: the Internet.
Some go even further to suggest that the Blockhain has the potential to reinvent key institutions. Ten years from now we will wonder how societies could have been survived without the Internet of Value. But let’s step one step back: What’s Blockchain?
Blockchain Is Like The European idea
Blockchain is the technology behind the digital currency Bitcoin, but Blockchain is unequal Bitcoin! The Blockchain is a kind of super sophisticated distributed ledger that keeps track of things on thousands or even millions of disparate computers, all coordinating with one another. Most simply, the Blockchain protocol is a cryptographically secure system of messaging and recording in a shared database.
Working in tandem, these systems enable a secure recording, verification and confirmation of transactions without the need of any single entity in charge. To write it in pictures: Today the Internet is an army with generals, we call them AGFA and the future?
The Blockchain is like the European idea – each encoded and work for the good of the whole: for a common decentral network.
Blockchain Is a Trust Machine
Using cryptography to maintain a peer-to-peer distributed, time-stamped and immutable consensus ledger of all past transactions. Each transaction is similar to a ledger item, which is aggregated with other blocks into a block of transactions, each connected to the last and needs to be agreed by consensus before adding to the chain. Transaction records cannot be forged, censored or reversed once a block is added. Transacting without trust and a third party becomes reality – with three main disruptive advantages:
– Trust: Less reliance on trusted third parties. Reducing or eliminating third party risk as trust is distributed over a decentral network
– Immutable Record: All participants share and consensually update the record. This permanent record imparts confidence in the provenance of value being transacted and enhances fraud detection
– Smart Contracts: Self-executing commitments. Obligations codified by smart contracts are easily replicable with the benefit of security, translucency and immutability of the Blockchain
Welcome To a Digital Borderless World
As blockchain develops, instead of having an internet that puts information and content online, we will get a system that essentially automates trust and verification. Information we now rely on accountants, banks, lawyers and governments to do. We will be able to know that anything on a Blockchain – land rights, money, a deed – is authentic and everyone around the world agrees on its value.
Facts & Figures: Blockchain Has Captured Venture Capital and Global Wallets
We saw over $1.4b in investments over the past three years – just in the first quarter of 2016 VC firms invested globally $160m into Blockchain startups, up from $26 million compared to the previous quarter regarding CB Insights and KPMG. Three significant funding rounds on Blockchain Startups – Circle with $60m (Series D), Digital Asset Holdings with $60m (Series A) and Blockstream with $55m (Series A) we have seen so far in 2016.
More than 2500+ Blockchain patents were globally filed over the last 3 years. 90+ central banks are engaged in Blockchain discussions worldwide as well as 90+ corporations have joined Blockchain consorts. Today, the pool of strategics investors in the Blockchain space has expanded from banks and VCs into insurance companies, payments and telcos.
But What Are The Use-cases?
Today use-cases are about Banking, or challenging the platform model, like Uber and AirBnB just to name a few. The Blockchain has the potential to eliminate intermediaries. Some other fascinating business concepts are about ownership and land rights or redefining the value chain of fair trade coffee. Software enabled contracts, called Smart Contracts, can verify if a job is made, and make the payment without a middleman.
Some InsurTech companies are even working to leverage Blockchain Technology as a mechanism for providing automatic payouts, particularly in the peer-to-peer insurance space where smart contracts could ensure payouts are made accurately and efficient. A song on the Blockchain could ask you to pay of it before it plays, cutting out Spotify and sending the money directly to the artist – fair trade music! Disruption. Furthermore Digital Identity will be a critical enabler to broaden applications to new verticals for instance a digital system for storing and transferring identity.
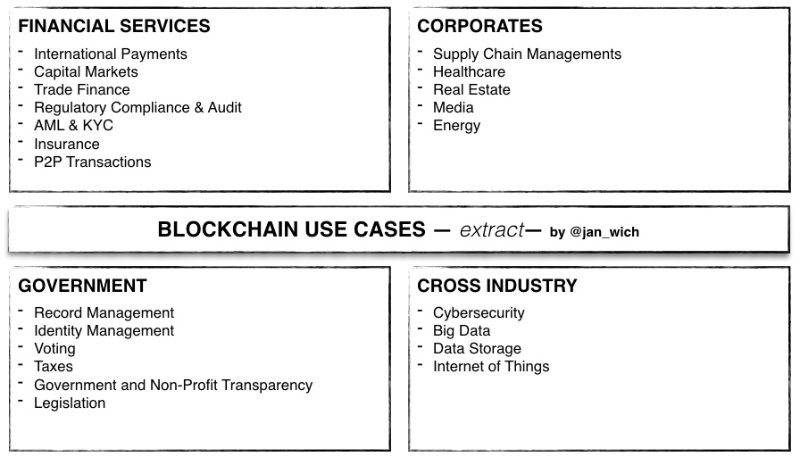
Graphic: Blockchain Use-Cases (extract), by @jan_wich
Currently VCs are betting its money especially on Blockchain Startups that are focusing on middleware and services, payments/remittance and capital market solutions.
Potential and Critics
The global discussions worldwide are growing significantly, but significant hurdles remain to large-scale implementation. An uncertain and unharmonized regulatory environment, nascent collective standardization efforts as well as an absence of formal legal frameworks draw the current situation.
The technology has the potential to drive simplicity and efficiency through the establishment of new infrastructure and processes across financial services and data driven businesses. Blockchain is not a panacea, but has the potential to redefine current processes and call into question today’s business models.
Honestly to catch the real impact of the Blockchain Technology is difficult. But – did we all know about TCP/IP and HTML once the internet had the breakthrough? No! Don’t struggle to understand the technology, search for the use-cases. Trial and Error. The Blockchain is more than a technology. It is a strategy.
Sources: Own research and ideas, WEF and CS
This article is first appeared on LinkedIn | Featured Image: Fotolia