Embedded Finance Total Market Value Could Reach US$7.2T by 2030
by Fintechnews Switzerland March 28, 2022The COVID-19 pandemic, accelerated digital adoption, and a maturing fintech infrastructure sector have fueled the popularity of embedded finance. By 2030, it’s projected that the total market value of the sector could reach US$7.2 trillion, surpassing the current value of all fintech startups and the top 30 global banks and insurers combined, a new report by Dealroom, a market intelligence company, and ABN AMRO Ventures, the corporate venture arm of ABN AMRO bank, says.
The report, titled The Rise of Embedded Finance, sums up key insights shared during a virtual forum hosted earlier this month that looked at the state of embedded finance and its growth prospects.
According to the report, embedded finance has the potential to unlock an opportunity bigger than the value of the entire fintech startup landscape and the top global banks and insurers, combined, which currently stands at US$7.1 trillion.
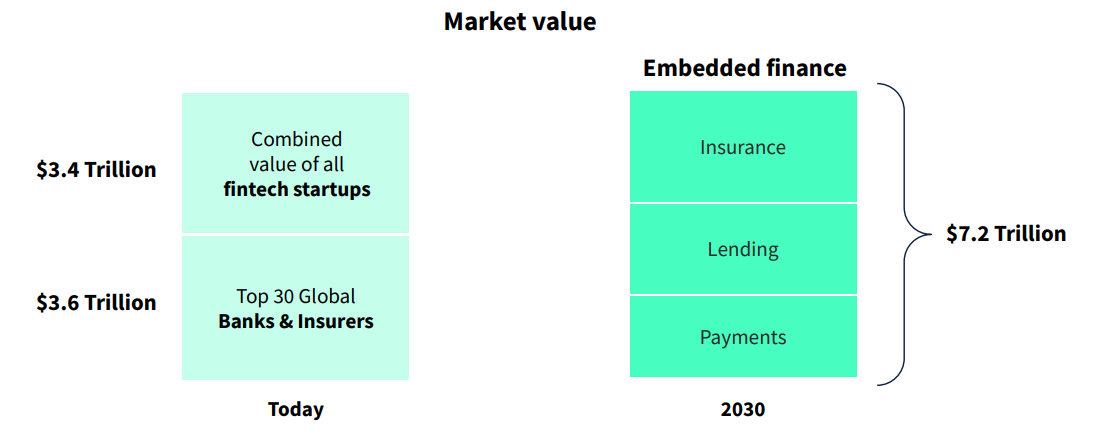
Embedded finance, a multi-trillion dollar opportunity, Source: The rise of embedded finance, Dealroom and ABN AMRO Ventures, 2022
Embedded finance, a concept referring to the seamless integration of financial services adopted by non-financial companies, has become a hot topic in the fintech space these past years. Companies from all industries and of all sizes have jumped on the bandwagon, aiming to capitalize on the accelerated shift to digital channels induced by the global pandemic, booming consumer of adoption of digital financial services, and customer demand for integrated experiences.
On the supply side, the maturing fintech infrastructure scene, which comprises companies providing key integrations and application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow other companies to build and offer their own fintech products and services to their customers, has further stimulated adoption.
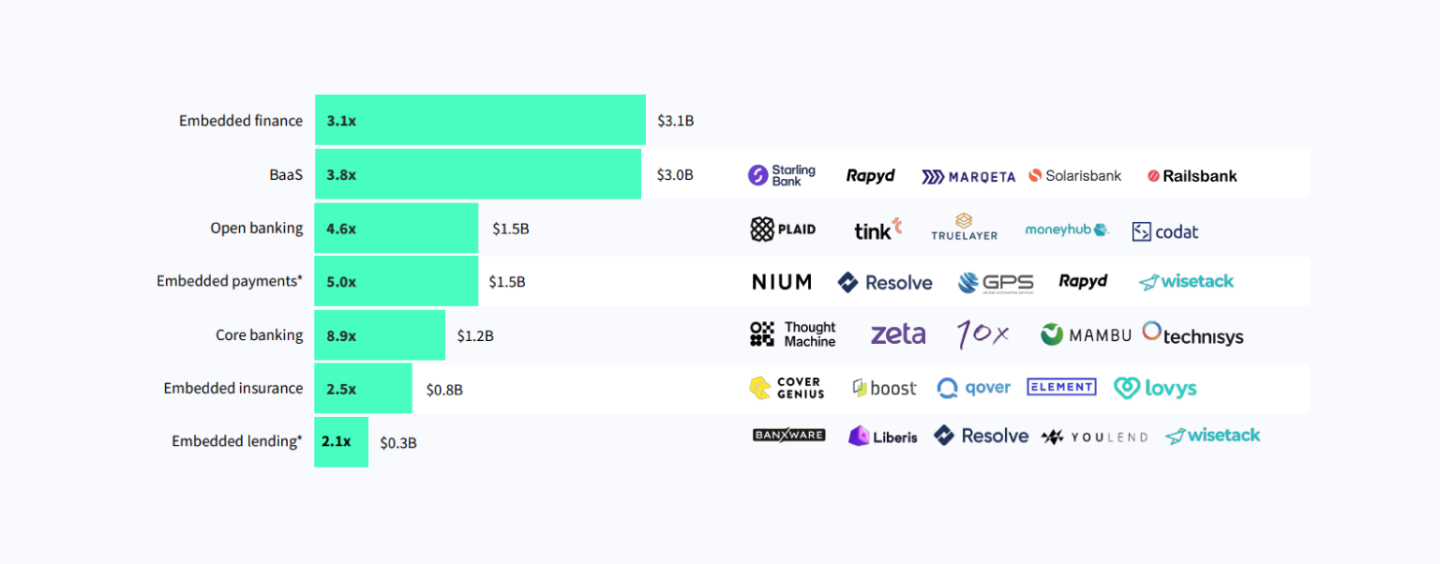
Evidenced of the rise of embedded finance is the surge in venture capital (VC) funding going into startups in the embedded finance and banking-as-a-service (BaaS) spaces, which grew by more than 3 times to US$3.1 billion and US$3 billion, respectively, between 2020 and 2021.
A look at the other trends comprising embedded finance shows that core banking recorded the strongest growth, with funding value growing 8.9 times to US$1.2 billion in 2021. Embedded payments (excluding independent buy now, pay later (BNPL) providers and not white-label products such as Klarna) saw the second biggest rise, growing 5 times to US$1.5 billion, followed by open banking, which rose 4.6 times to US$1.5 billion as well as.
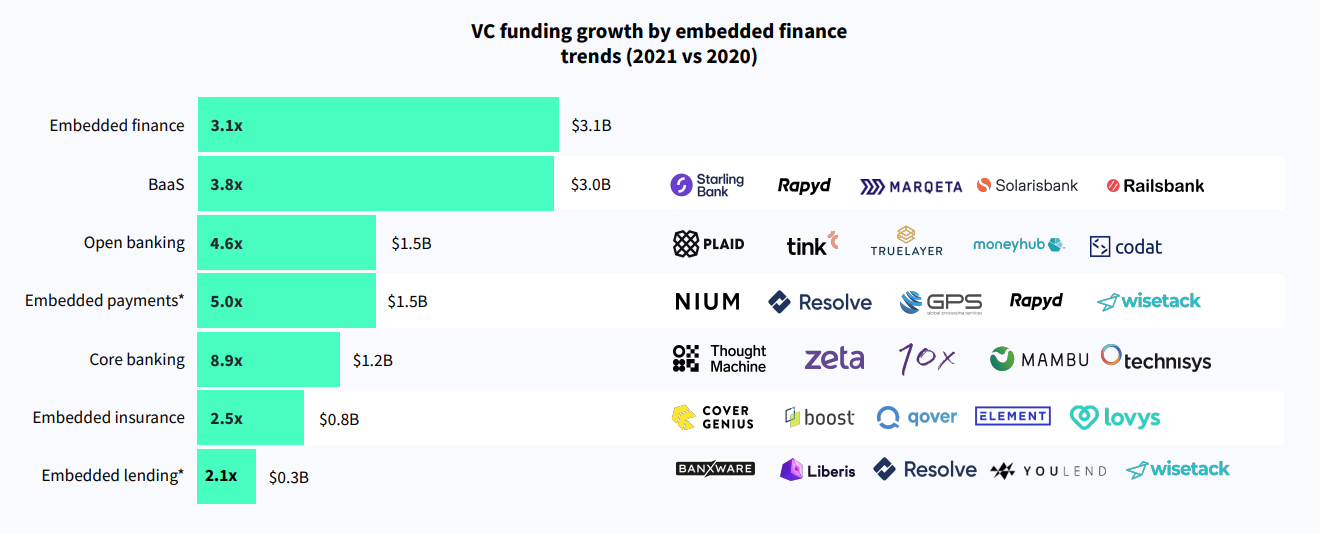
VC funding growth by embedded finance trends (2021 vs 2020), Source: The rise of embedded finance, Dealroom and ABN AMRO Ventures, 2022
At the bottom of the list, embedded insurance and embedded lending saw the smallest growth, with, nevertheless, funding rising 2.5 times and 2.1 times, respectively. At US$800 million raised by embedded insurance startups in 2021, and US$300 million raised by embedded lending startups, these two sub-segments are still rather nascent, despite their huge potential.
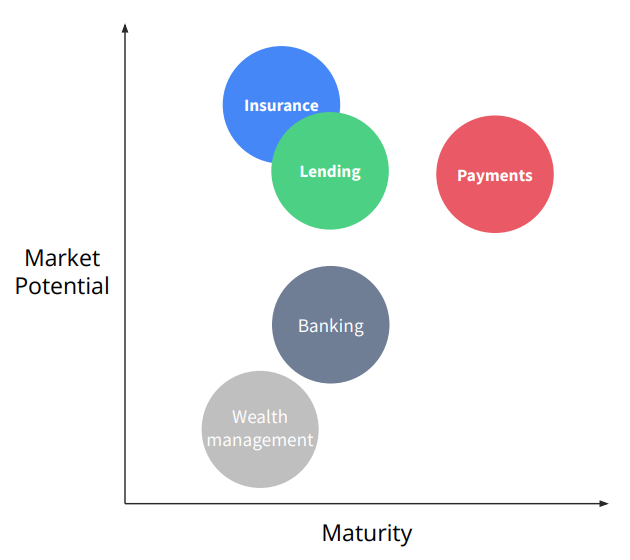
Embedded finance maturity and potential by use case, Source: The rise of embedded finance, Dealroom and ABN AMRO Ventures, 2022
A separate study by Mambu and Amazon Web Services (AWS), from which the US$7.2 trillion market opportunity forecast was taken from, suggests that embedded lending (e.g. working capital for merchants, and consumer financing at point of sale (POS) and checkout) could be worth US$3.4 billion by 2030, making it the largest market opportunity.
Meanwhile, embedded insurance (e.g. health insurance integrated into fitness apps, and property and casualty (P&C) insurance integrated into e-commerce and business trade platforms) could be worth US$1.8 trillion by 2030.
Looking at each key sector’s projected uptake of embedded finance, retail and e-commerce is expected to be the biggest adopter, accounting for 49% of the market, or US$3.5 trillion, by 2030. Healthcare is the second largest potential sector at 17% or US$1.7 trillion.
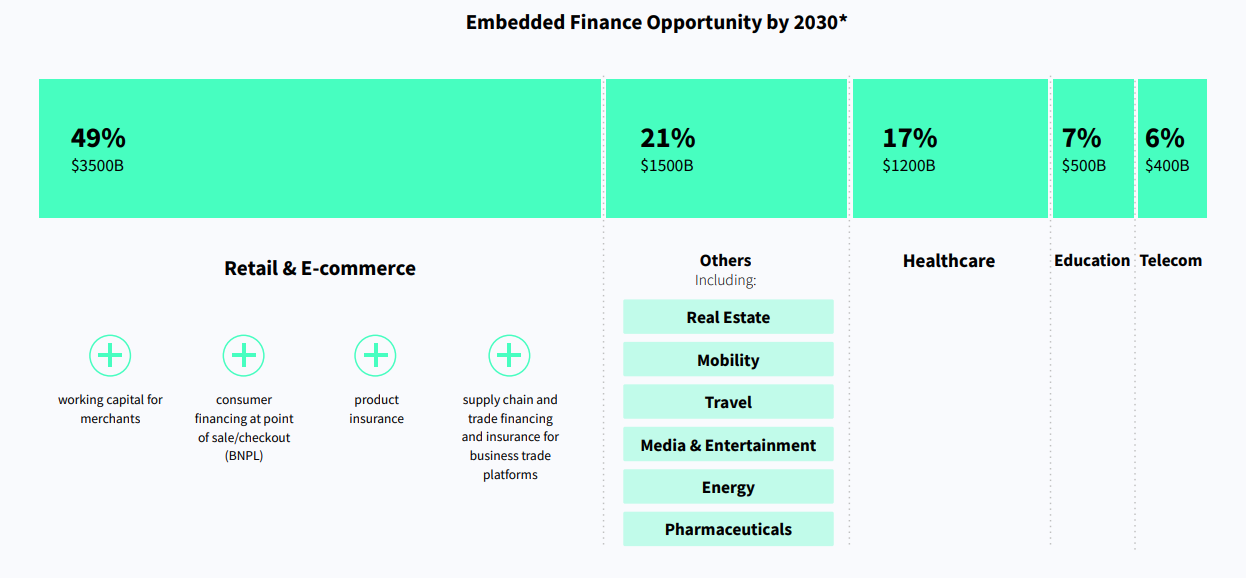
Embedded Finance Opportunity by 2030, Source: The rise of embedded finance, Dealroom and ABN AMRO Ventures, 2022
In Switzerland, fintech providers are catching up to the embedded finance movement, with wealthtech provider Additiv, for example, doubling down on the trend. Over the past, the firm has ramped up its Asia Pacific (APAC) team as it seeks to tap into the region’s estimated US$32 billion per annum opportunity. Meanwhile, Swiss regtech company Apiax has been marketing itself as an “embedded compliance” specialist that provide banks, wealth managers and asset managers with a comprehensive compliance to deploy across their whole organization.





